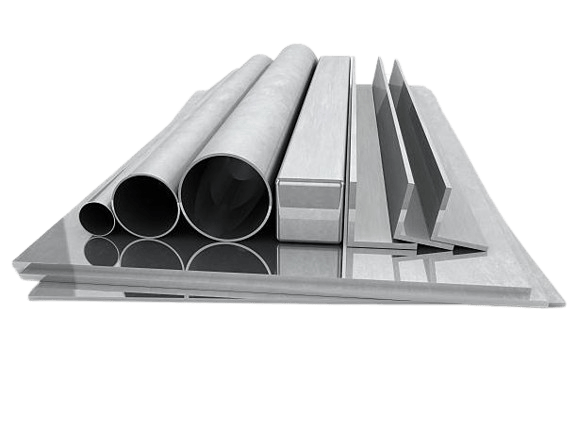
When purchasing aluminum products, choosing between wrought aluminium and cast aluminum can be challenging, as these two types of aluminum demonstrate distinct advantages across various industries. In this blog, we will introduce wrought aluminium and compare it to cast aluminum.
What Is Wrought Aluminum?
Wrought aluminum stands as an aluminum alloy crafted through the meticulous mechanical manipulation of pure aluminum ingots that have undergone smelting and alloying processes. This refined metal is meticulously shaped into billets or slabs, subsequently undergoing rolling, forging, or extrusion techniques to achieve the precise desired form and structure.
Wrought Aluminium Grades
The selection of wrought aluminum alloys such as 6061, 2024, 7075, and 7050 is based on specific requirements in various industries.Different aluminum alloys have varying requirements for the wrought process based on their specific compositions and intended applications. Here are the general conditions specific aluminum alloys need to be wrought:
6061 Wrought Aluminium
In the wrought process of the 6061 aluminum alloy, temperatures ranging between 400°C to 500°C are commonly applied to enhance its formability. This alloy undergoes mechanical shaping through methods like rolling, extrusion, or forging to meet specific design requirements. Additionally, annealing treatments are crucial to improve formability and reduce internal stresses within the material.
2024 Aluminum Wrought
For the 2024 aluminum alloy, heating to temperatures around 470°C is essential to achieve optimal formability. This alloy, known for its strength and fatigue resistance, is typically forged to shape it according to desired specifications. Annealing processes play a critical role in maintaining the alloy’s ductility and preventing cracking during forming operations.
7075 Wrought Aluminum
In the case of the 7075 aluminum alloy, heating within the temperature range of 440°C to 500°C is necessary for shaping purposes. This high-strength alloy is commonly processed through forging or extrusion methods to leverage its exceptional mechanical properties. Furthermore, precise heat treatment procedures are vital to enhance the alloy’s strength and hardness effectively.
7050 Wrought Aluminium
When working with the 7050 aluminum alloy, specific temperature treatments are employed to ensure formability while preserving its strength characteristics. The alloy is often shaped through the forging process due to its superior strength and toughness attributes. Implementing precise heat treatment protocols is crucial to optimize the properties of the 7050 alloy for applications requiring high stress tolerance.
What Are The Advantages Of Wrought Aluminium?

Wrought aluminium offers a range of advantages in industrial production:
- Retained Mechanical Properties: Wrought aluminum maintains its mechanical properties well due to the mechanical forming processes it undergoes, resulting in enhanced strength and durability in the final product.
- Improved Structural Integrity: Wrought aluminium products exhibit superior structural integrity, as controlled forming processes eliminate casting defects like porosity and alloy segregation, ensuring a more reliable end product.
- Superior Surface Finish: Wrought aluminum typically showcases better surface finishes, an advantageous feature for applications where aesthetics and surface quality are crucial.
- Enhanced Manufacturing Techniques: Wrought aluminum is well-suited for various manufacturing techniques such as welding, machining, and forming, thanks to its consistent properties that facilitate easier processing in production.
Wrought Aluminum Applications

Aerospace: In the aerospace and airline sectors, high-performance wrought aluminum alloys like 7075 are extensively used. The high strength-to-weight ratio of wrought aluminium makes it ideal for aerospace applications where durability and lightweight materials are crucial.
Transportation: Wrought aluminum plays a significant role in the transportation industry, enhancing fuel efficiency in cars and motorcycles while ensuring safety, reliability, and durability. Aluminum is also preferred in trains and subway cars for its strength, environmental benefits, and visual appeal.
Architecture and Construction: Aluminum has revolutionized the architecture and construction sectors. Its use in extrusions allows for the creation of various structural elements like window frames and fixtures for modern skyscrapers, showcasing both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Electronics and Appliances: Wrought aluminum is utilized in electrical conductors, cooking utensils, appliances, welding rods, beverage cans, pressure vessels, medical instruments, and a variety of electrical devices, benefiting from its lightweight nature and corrosion resistance.
Wrought vs Cast: What's The Difference?

The difference between wrought aluminum and cast aluminum lies in various aspects:
Wrought vs Cast: Alloying Elements Percentage
Wrought aluminum typically contains about 85% aluminum, with a smaller percentage of alloying elements. In contrast, cast aluminum has a larger proportion of alloying elements in its composition.
Cast vs Wrought: Thickness
Cast aluminum alloys tend to be thicker and heavier, while wrought alloys can be obtained in thinner forms, even down to foil thickness.
Wrought vs Cast: Precision
Cast aluminum alloys, despite their lower tensile strength, can achieve high precision due to the various defects present. Wrought alloys, due to their ability to undergo processes like drilling, milling, and grinding, are better suited for dimensional accuracy and precision parts.
Wrought vs Cast: Melting Point
Cast aluminum alloys have a lower melting point, contributing to their cost-effectiveness. Wrought aluminum alloys, with a higher melting point, are less cost-effective in terms of production.
Cast vs Wrought: Internal and External Defects
Wrought alloys are generally free of external and internal defects, while cast aluminum alloys often exhibit numerous defects both externally and internally.